Six Sigma DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)
About Course
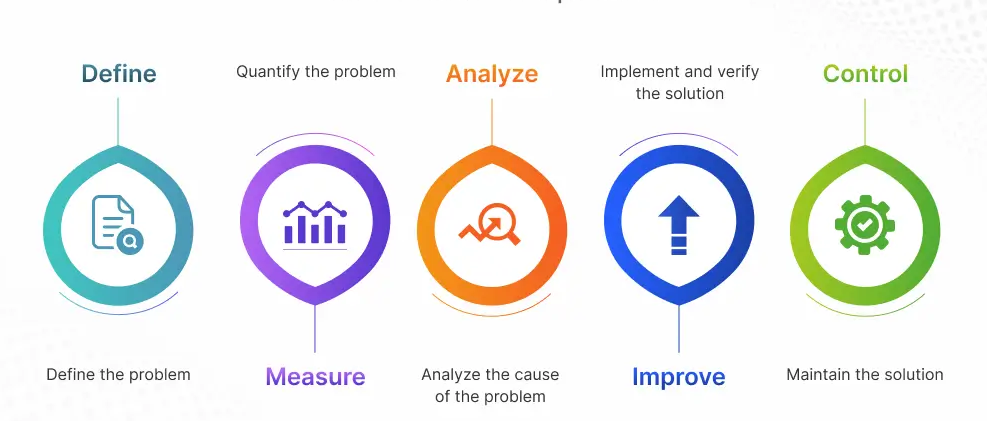
Six Sigma DMAIC is a structured, data-driven methodology used for process improvement. DMAIC stands for:
Define: Identify the problem or process that needs improvement, set project goals, and outline the scope.
Measure: Collect data to establish baselines, understand current performance, and quantify the problem. For example, measuring the average turnaround time for policy renewals.
Analyze: Examine the data to identify root causes of inefficiencies or risks. This might involve analyzing claims data to uncover bottlenecks or sources of errors.
Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address root causes. For example, streamlining workflows or introducing new digital tools to reduce manual errors.
Control: Put controls in place to sustain improvements, such as regular monitoring, updated procedures, or dashboards for ongoing performance tracking.
Course Content
Define
Measure
Analyze
Improve
Control
Student Ratings & Reviews

